Inner ear pressure, often experienced as fullness, popping, or discomfort, can be more than just a fleeting annoyance. For many, it becomes a persistent issue that affects balance, hearing clarity, and overall quality of life. At Lavender Family Chiropractic in Sarasota, Florida, we recognize that resolving inner ear pressure often requires looking beyond the ear itself.
Through precise upper cervical chiropractic care and advanced diagnostic tools like 3D cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), we aim to identify and correct the root cause of the problem—often stemming from subtle misalignments in the upper neck that interfere with the nerves and circulatory pathways servicing the inner ear. In this extensive guide, we’ll explore the physiology of inner ear pressure, common and lesser-known causes, the role of upper cervical misalignment, and how Lavender Family Chiropractic’s gentle, targeted approach can help. We’ll also answer the top 15 frequently asked questions about ear pressure to empower you with the knowledge you need to seek effective relief.
If you want to read more after this blog, click Here
Table of Contents
- Anatomy & Physiology of Inner Ear Pressure
- Common Causes of Inner Ear Pressure
- Upper Cervical Misalignment and Ear Pressure
- Introduction to Upper Cervical Chiropractic Care
- Lavender Family Chiropractic’s Approach
- CBCT Scanning: Precision Diagnostics
- Case Example: Resolving Chronic Ear Pressure
- Top 15 FAQs About Inner Ear Pressure
- Conclusion and Next Steps
1. Anatomy & Physiology of Inner Ear Pressure
The inner ear comprises intricate structures responsible for both hearing and balance. Key components include:
- Cochlea: A fluid-filled, spiral-shaped chamber that translates sound waves into nerve signals.
- Vestibular System: A trio of semicircular canals and otolith organs (the saccule and utricle) that detect head movement and orientation relative to gravity.
- Eustachian Tube: A narrow channel connecting the middle ear to the back of the throat, which regulates middle ear pressure by allowing fluid and air to equalize.
Under normal conditions, the fluids in the cochlea and vestibular system maintain precise pressure balances to facilitate hearing and equilibrium. When this balance is disrupted—due to fluid retention, inflammation, or impaired drainage—pressure changes can lead to symptoms such as fullness, popping sounds, dizziness, and sometimes hearing fluctuations.
Neurologically, the inner ear structures communicate via the vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII) with the brainstem, which integrates auditory and balance information. Vascularly, tiny arteries from the vertebral and basilar systems supply this region; even slight alterations in blood flow dynamics can influence inner ear fluid homeostasis.
Understanding this interplay between mechanical, neurological, and vascular factors underscores why addressing only the ear may not fully resolve inner ear pressure issues.
2. Common Causes of Inner Ear Pressure
While the sensation of ear fullness is common, persistent pressure often indicates an underlying dysfunction. Common and notable causes include:
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD)
- When the Eustachian tube fails to open properly, air becomes trapped in the middle ear, leading to pressure differentials. Allergies, colds, and sinus infections are frequent culprits.
- Middle Ear Infections (Otitis Media)
- Fluid accumulation and inflammation during ear infections increase pressure, causing pain and muffled hearing.
- Barotrauma
- Rapid pressure changes (e.g., during airplane descent or scuba diving) can overwhelm the ear’s ability to equalize, resulting in discomfort or injury to middle and inner ear structures.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Dysfunction
- Misalignment or muscle tension in the jaw joint places stress on adjacent structures, including the Eustachian tube and middle ear, thereby influencing pressure sensations.
- Allergies and Sinus Congestion
- Nasal and sinus inflammation can obstruct the Eustachian tube, causing pressure buildup behind the eardrum.
- Meniere’s Disease
- An inner ear disorder characterized by abnormal endolymph fluid accumulation, leading to episodic vertigo, hearing fluctuations, tinnitus, and ear fullness.
- Acoustic Neuroma
- Although rare, a benign tumor on the vestibulocochlear nerve can manifest with ear fullness, tinnitus, hearing loss, and balance disturbances.
- Superior Canal Dehiscence
- A thinning or opening in the bony canal above the superior semicircular canal can alter fluid pressures, resulting in autophony (hearing internal sounds) and a sense of ear fullness.
- Cervicogenic Factors
- Misalignments of the upper cervical spine (C0–C2) can affect neural pathways and blood vessels servicing the inner ear, leading to chronic pressure sensations without obvious local ear pathology.
Recognizing the diversity of potential causes highlights the necessity of a thorough and holistic evaluation. In many chronic or recurrent cases, traditional ENT approaches provide symptomatic relief but may not uncover biomechanical contributors—an area where upper cervical chiropractic care excels.
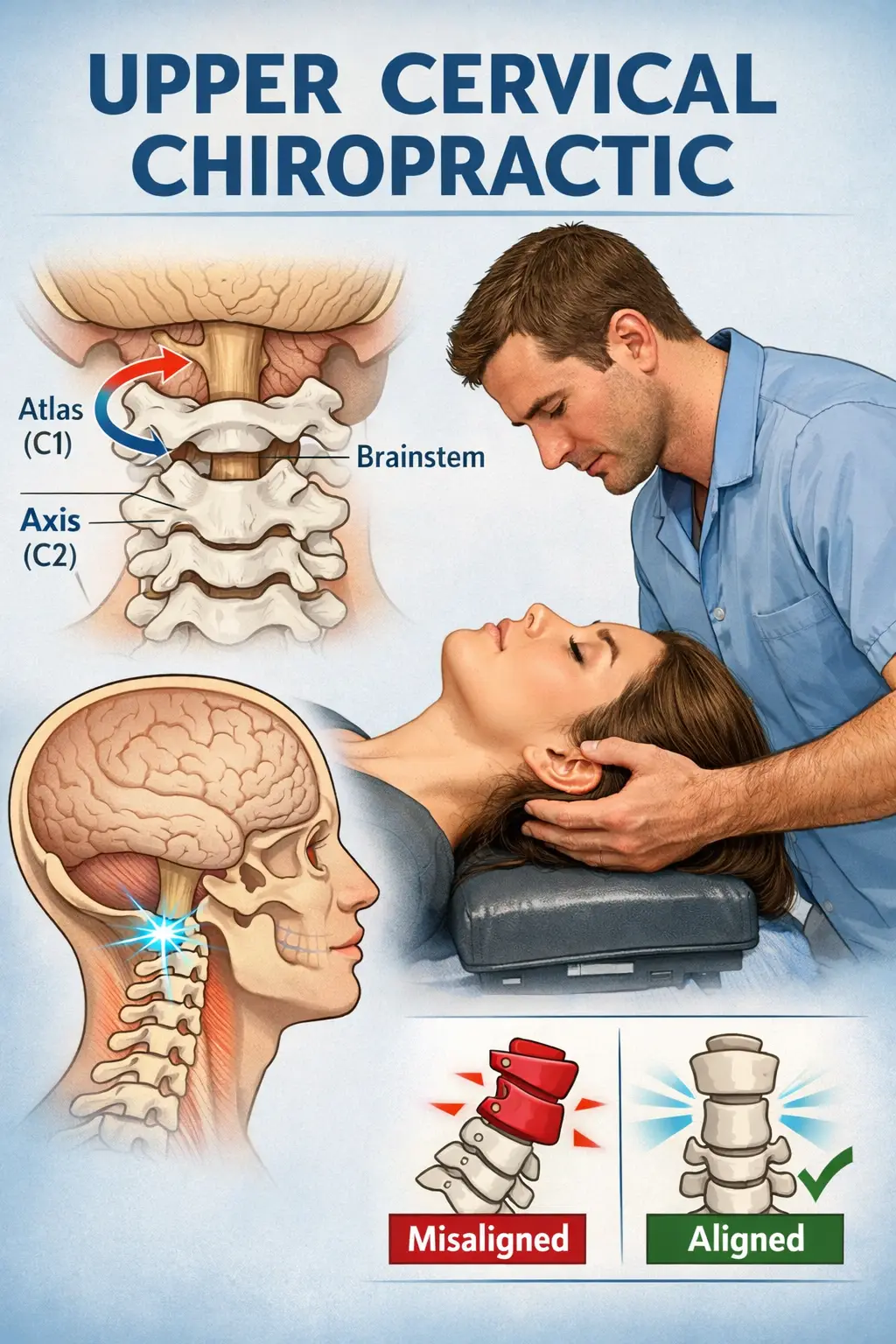
3. Upper Cervical Misalignment and Ear Pressure
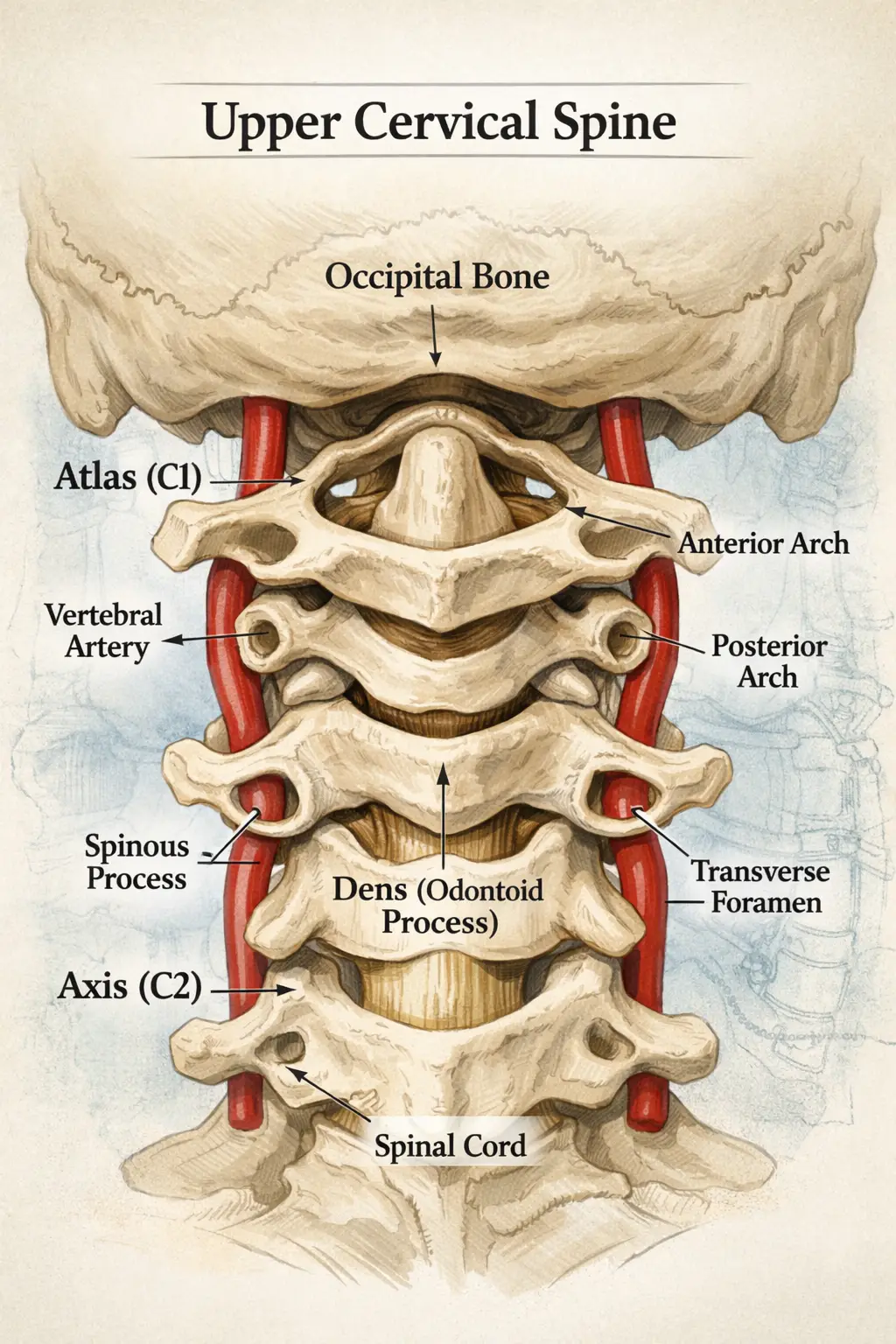
The upper cervical spine—the junction of the skull (occiput) and the first two cervical vertebrae (C1 or atlas, and C2 or axis)—houses critical neurological and vascular structures:
- Brainstem Connection: The spinal cord transitions to the brainstem at this level, making it a conduit for cranial nerve function.
- Vertebral Arteries: These arteries ascend through the transverse foramina of C1 and C2 before entering the skull to supply the brainstem and inner ear.
- Suboccipital Musculature: Tightness or spasms in the muscles surrounding C1–C2 can distort joint mechanics and pressure relationships.
When the atlas or axis shifts even fractionally, it can place abnormal tension on the dura mater and stretch or compress neural elements. This can manifest as:
- Altered vestibular nerve signaling, leading to pressure sensations and dizziness.
- Impaired blood flow through the vertebral arteries, causing ischemic changes in the labyrinth fluid dynamics.
- Tension on connective tissues that interface with the Eustachian tube and middle ear structures.
Clinical studies have linked cervical spine misalignments with symptoms of ear fullness, tinnitus, and vertigo. By precisely correcting these misalignments, upper cervical chiropractic care aims to normalize biomechanics, restore proper blood flow, and facilitate neurological function—addressing the root cause rather than merely masking symptoms.
4. Introduction to Upper Cervical Chiropractic Care
Upper cervical chiropractic is a specialized discipline focusing on the precise alignment of C1 (atlas) and C2 (axis). Key principles include:
- Gentle, Non-Forceful Adjustments: No twisting, cracking, or popping; adjustments are delivered with low-force impulses tailored to each patient’s anatomy.
- Specificity: Using advanced measurement and analysis—such as digital postural assessment, thermography, and digital x-rays—to determine the exact vector and magnitude of misalignment.
- Neurological Focus: Recognizing that spinal alignment directly impacts neural pathways and cerebrospinal fluid flow, which influence systemic health.
Benefits of upper cervical chiropractic for inner ear pressure:
- Improved Eustachian Tube Function: By alleviating cervical tension and restoring normal muscular tone, drainage and equalization often improve.
- Enhanced Blood Flow: Correction of vertebral artery kinks or obstructions can normalize labyrinthine circulation, stabilizing inner ear fluid pressures.
- Balanced Neural Signaling: Reducing nerve tension helps recalibrate vestibular and cochlear nerve function, decreasing aberrant pressure sensations.
At Lavender Family Chiropractic, our upper cervical protocols are designed to be safe, precise, and effective, with a focus on long-term structural stability rather than short-term relief.
5. Lavender Family Chiropractic’s Approach
Lavender Family Chiropractic in Sarasota, Florida, integrates cutting-edge diagnostics and a patient-centered philosophy to address inner ear pressure:
- Comprehensive History & Examination
- Detailed review of symptoms, triggers, and previous treatments.
- Assessment of head posture, spinal alignment, and range of motion.
- Digital Postural and Thermographic Analysis
- Non-invasive scans to detect heat asymmetries and postural deviations indicative of neurological stress.
- 3D CBCT Imaging
- Cone beam computed tomography provides a three-dimensional view of cervical bone structures, revealing subtle misalignments invisible on standard x-rays.
- Enables measurement of joint spacing, vertebral rotation, and spatial relationships with precision down to fractions of a millimeter.
- Tailored Upper Cervical Adjustments
- Using orthogonal adjusting instruments or manual contacts, our chiropractors deliver adjustments calibrated to each patient’s unique anatomy.
- No cracking or twisting—just precise, gentle impulses that align the atlas and axis.
- Ongoing Monitoring & Support
- Periodic reevaluations using posture photos and thermography ensure that alignment improvements are maintained.
- Nutritional guidance, balance exercises, and ergonomic recommendations support overall recovery.
Patients frequently report reduced ear fullness, improved hearing clarity, and diminished dizziness after initiating upper cervical care. By focusing on the root cause—cervical misalignment—Lavender Family Chiropractic helps restore natural balance and ear pressure regulation.
6. CBCT Scanning: Precision Diagnostics
Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) is revolutionizing chiropractic diagnostics by providing:
- 3D Visualization: Unlike two-dimensional x-rays, CBCT captures volumetric data of the cervical spine, revealing aberrations in any plane.
- Detailed Measurements: Software tools measure joint angles, vertebral offsets, and rotational deviations with unprecedented accuracy.
- Enhanced Safety: Lower radiation exposure compared to medical CT scans, with doses similar to or lower than multiple conventional x-rays.
How CBCT Helps With Inner Ear Pressure:
- Identifying Vertebral Artery Kinks: Misalignments that impinge or compress vertebral arteries can be clearly visualized.
- Quantifying Misalignment: Understanding millimeters of offset guides the chiropractor to apply the correct adjustment vector.
- Tracking Progress: Follow-up CBCT imaging demonstrates structural improvements, correlating with symptomatic relief.
At Lavender Family Chiropractic, CBCT is an integral part of our diagnostic toolkit, ensuring that every adjustment is backed by precise anatomical data and that patients receive the most informed care possible.
7. Case Example: Resolving Chronic Ear Pressure
Patient Profile:
- Age/Gender: 45-year-old female
- Chief Complaint: Persistent left ear fullness for 18 months, neck pain, resistant to multiple ENT treatments including decongestants, nasal sprays, and Eustachian tube balloon dilation.
- Additional Symptoms: Intermittent tinnitus, mild dizziness when turning head.
Findings:
- Digital posture analysis showed a 12 mm right head translation.
- Thermography revealed heat asymmetry at C1–C2
- CBCT imaging demonstrated a 3.5 mm lateral shift of the atlas and a slight rotational misalignment of the axis.
Intervention:
- Gentle upper cervical adjustments delivered weekly for four weeks, targeting the precise vectors identified on CBCT.
- Patient education on sleep posture and ergonomic workstation setup.
- Vestibular exercises to support balance retraining.
Outcome:
- By week three, the patient reported 50% reduction in ear fullness.
- At week six, ear pressure resolved completely, tinnitus decreased by 80%, and dizziness episodes ceased.
- Follow-up CBCT at three months confirmed sustained atlas alignment.
This case highlights the power of combining advanced imaging with gentle upper cervical correction to address chronic inner ear pressure at its source.
8. Top 15 FAQs About Inner Ear Pressure
Below are the most frequently asked questions we receive at Lavender Family Chiropractic regarding ear pressure. Each answer provides insight to help you better understand your condition and treatment options.
1. What is causing my ear to feel “full” all the time?
Persistent ear fullness often indicates pressure imbalance in the middle or inner ear. While ETD and fluid buildup are common culprits, upper cervical misalignments can also contribute by disrupting nerve and vascular function to the ear. A thorough evaluation helps distinguish among these causes.
2. How is inner ear pressure different from middle ear pressure?
Middle ear pressure relates to the air-filled space behind the eardrum, regulated by the Eustachian tube. Inner ear pressure involves the fluid-filled cochlea and vestibular system. Disturbances in either can cause fullness, but inner ear issues often accompany balance symptoms like dizziness.
3. Can allergies cause ear pressure?
Yes. Allergic inflammation can block the Eustachian tube, leading to middle ear pressure. Additionally, sinus congestion can alter intracranial and inner ear fluid dynamics, contributing to a feeling of fullness. Addressing sinus health is an important part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
4. What role does the Eustachian tube play in ear pressure?
The Eustachian tube equalizes air pressure between the middle ear and the back of the throat. When it fails to open properly—due to inflammation, anatomical blockage, or muscular dysfunction—air becomes trapped, creating negative or positive pressure that feels like fullness.
5. Are there simple at-home remedies for ear fullness?
Home strategies include:
- Gentle swallowing or yawning to open the Eustachian tube
- Valsalva maneuver (exhaling gently while pinching the nose and closing the mouth)
- Nasal decongestants or saline irrigation for congestion relief
However, persistent symptoms warrant professional evaluation to rule out underlying causes.
6. How can upper cervical chiropractic care relieve ear pressure?
By realigning C1 and C2, upper cervical care alleviates tension on the dura mater and normalizes vertebral artery flow, improving both neurological and vascular input to the ear. This combined effect helps restore proper fluid pressure balance in the auditory and vestibular systems.
7. Is CBCT safe for imaging my neck?
Yes. CBCT uses low-dose radiation—often comparable to or less than standard dental x-rays. It provides high-resolution, three-dimensional views of cervical structures, making it a safe and informative diagnostic tool in chiropractic care.
8. How many chiropractic visits will it take?
Every patient is unique. Some experience relief within 2–4 visits, while others may require 6–8 sessions to achieve and stabilize alignment. After initial corrective care, maintenance visits every few months help ensure long-term results.
9. Can chiropractic care prevent ear infections?
While upper cervical chiropractic isn’t a substitute for medical management of infections, improved fluid drainage and immune function via better nerve signaling can reduce the frequency and severity of ear infections in many patients.
10. What if I also have tinnitus or dizziness?
Tinnitus and dizziness often accompany ear pressure, especially when the vestibular apparatus is affected. By restoring proper joint alignment and blood flow, upper cervical care can decrease tinnitus volume and frequency of dizzy spells for many patients.
11. Are there any contraindications?
Upper cervical chiropractic is safe for most patients. Contraindications include unstable spinal fractures, severe osteoporosis, or certain vascular anomalies. Comprehensive initial screening ensures appropriate care planning.
12. Will I hear a “pop” when adjusted?
No. Upper cervical adjustments at Lavender Family Chiropractic are delivered using gentle instrument or hand contacts without high-velocity thrusts. You won’t experience the traditional “cracking” sound often associated with general chiropractic.
13. How does sleep posture affect ear pressure?
Sleeping with the head propped too high or on one side can exacerbate cervical misalignments and impede lymphatic drainage around the ear. We provide ergonomic pillow recommendations and sleep posture coaching to support healing.
14. Can stress influence ear pressure?
Absolutely. Stress increases muscle tension in the neck and jaw, interfering with Eustachian tube function and vertebral artery flow. Incorporating relaxation techniques and stress management is part of our holistic approach.
15. What should I expect during my first visit?
Your initial appointment includes a detailed history, postural exam, thermographic scan, and potentially CBCT imaging. After reviewing findings with you, we’ll perform your first gentle adjustment and discuss a personalized care plan.
9. Conclusion and Next Steps
Inner ear pressure is a multifaceted issue that often resists one-size-fits-all solutions. While traditional ENT treatments focus on local symptoms, underlying biomechanical and neurological factors—especially upper cervical misalignment—can play a critical role. At Lavender Family Chiropractic in Sarasota, Florida, our specialized upper cervical care, supported by advanced CBCT diagnostics, aims to restore alignment, optimize nerve and vascular function, and address ear pressure at its root.
If you’re struggling with persistent ear fullness, popping, or associated dizziness and tinnitus, we invite you to schedule a comprehensive evaluation. Let us help you achieve lasting relief through gentle, precise adjustments tailored to your unique anatomy. Your journey to balanced ear pressure and improved quality of life begins with a single step—contact Lavender Family Chiropractic today.
Schedule With Us!
Lavender Family Chiropractic in Sarasota Florida offers complimentary consultations to learn more about you. Click the link below!
https://intake.chirohd.com/new-patient-scheduling/724/lavender-family-chiropractic
Visit our Website!
To learn more about us go to http://www.chiropractorsarasotaflorida.com
We also service Bradenton, Parrish, Ellenton, Ruskin, Venice, Tampa, St. Pete, Osprey, Longboat, Lakewood Ranch, Myakka City.
If you are not local, visit www.uccnearme.com to find a doctor in your area!